You probably already know that sunscreen is an absolute must. Too much sun can ruin an otherwise good outing. Worse, there is evidence that it can cause skin damage, premature aging and skin cancer. Our body requires the sun to produce vitamin D, but there is a balance between sufficient exposure to sunlight and getting too much!
But with all the sunscreen choices available today, how do you choose?
These are the best advices on choosing and using sunscreen for smart-aging:
1. Choose Broad Spectrum
Two types of UV light are proven to contribute to the risk for skin cancer:- Ultraviolet A (UVA) has a longer wavelength, and is associated with skin aging.
✔ UVA rays, while slightly less intense than UVB, penetrate your skin more deeply.
✔ UVA accounts for up to 95 percent of the UV radiation reaching the earth. These rays maintain the same level of strength during daylight hours throughout the year. This means that during a lifetime, we are all exposed to a high level of UVA rays.
✔ UVA can penetrate windows and cloud cover.
✔ Exposure causes genetic damage to cells on the innermost part of your top layer of skin, where most skin cancers occur. The skin tries to prevent further damage by darkening, resulting in a tan. Over time, UVA also leads to premature aging and skin cancer.
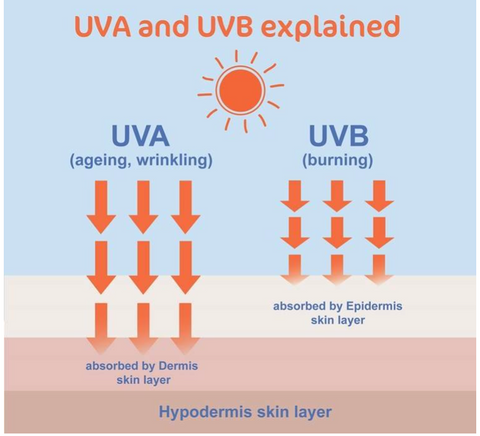
- Ultraviolet B (UVB) has a shorter wavelength and is associated with skin burning.
✔ UVB penetrates and damages the outermost layers of your skin.
✔ UVB is connected to the Sun Protection Factor (SPF) on labels of sunscreen products. The SPF number tells you how long the sun’s radiation (including some of the UVA) would take to redden your skin when using that product compared to the time without sunscreen.
✔ UV exposure that leads to sunburn has proven to play a strong role in developing melanoma, the most dangerous of the three most common types of skin cancer.
2. Two types of sunscreens:
- Physical (mineral) sunscreen ingredients, also known as the ‘Mineral sunscreens’, contain inorganic physical UV filters that create a barrier on the skin that filter out UV rays before they penetrate into the skin.
☼ Physical sunscreens are sometimes called SUN BLOCKERS.
☼ They use mineral-based ingredients, like titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, to block UV rays.
☼ Physical sunscreens work by staying on top of the skin to deflect and scatter damaging UV rays away from the skin.

- Chemical sunscreen ingredients, on the other hand, contain organic carbon-based active ingredients designed to absorb UV radiations upon contact.
☼ Chemical sunscreens actually penetrate deep into the epidermis and dermis layer of the skin and hence called SUN FILTERS.
3.
Aim for at least SPF 30 or higher.
Studies show that higher number SPF sunscreens are more effective at preventing sunburn.
What does SPF mean?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor.The number tells you how long the sun’s UVB rays would take to redden your skin if you apply the sunscreen exactly as directed compared with the amount of time without sunscreen. So, if you use an SPF 30 product properly, it would take you 30 times longer to burn than if you used no sunscreen.
4. Lay it on thick.
Most of us typically apply only 1/4 to 1/2 of the amount of sunscreen we are supposed to use to get the right protection. While lotions are often preferred over sprays, if you are using a spray, the rule of thumb is to spray until it glistens and then rub it in evenly.
For creams and lotions, it should take a full ounce to cover your entire body. If you haven’t gone through your bottle of sunscreen at the end of the summer you likely aren’t using enough.
It's okay to apply more sunscreen than you should. Better to apply too much than not enough.

5. Cover ALL areas that will be exposed to the sun.
Remember areas such as the tops of your feet, neck, tips of your ears, and the part in your hair. They often get forgotten. Putting it on before your bathing suit will help you make sure you are well covered.
6. Reapply every two hours.
If you’re swimming or sweating, you’ll want to reapply sunscreen more often because it washes off and loses its effectiveness.
7. People with darker skin tones should wear sunscreen too.
8. Don't rely on your cosmetic alone to offer adequate sun protection.
9. There are other ways beyond sunscreen to protect your skin from the sun, such as:
★ Stay inside when the sun is at its most intense—from 10 a.m.-2 p.m.
★ Seek the shade.
★ Cover up with long sleeves/pants/a broad-brimmed hat (4-inch+ brim).
★ Wear protective clothing with a UPF rating.
Don't forget to get our Moisturizing Daily Sunscreen SPF 50, Broad Spectrum.


Comments (0)
Back to Blog